
Table of contents
SD card stands for the secure digital card. If you own a digital camera, you have a slot for a memory card. SD cards are the most popular cards used in digital photography. No matter what type of digital device you’re using. You always need some storage device to store your data. Even if your phone or tablet has a built-in memory feature, chances are you need to expand your storage capacity by using a memory card or any other external storage media.
Of all the data storage options available, memory cards in general are the most widely used. However, despite their popularity and extensive usage, not many people know what memory cards are and how they work. The terms memory cards and SD cards are often used as synonyms. But the truth is that memory card is a broader category, and SD card is only one type of memory card. Also, users often get confused between SD cards and MicroSD cards. So, to clear all the confusion, here we have explained everything you need to know about SD cards – the most popular type of memory card.
Understanding of SD card
Secure Digital Card is a removable storage device of the size of a postage stamp or smaller. SanDisk, Panasonic, and Toshiba jointly developed this type of memory card to hold data. Introduced in 1999, SD cards quickly became an industry standard and widely used in portable devices. Later, the developers formed the SD Association to promote and enforce SD card standards across the industry. Founded in January 2000, the SD Association does not manufacture or sell any product. It only develops and promotes memory card storage standards. The reliability of SD cards may differ based on the brand.
An SD Card is a tiny flash memory card designed for high-capacity memory. This flash memory card can be used in various portable devices to expand their storage capacities, such as car navigation systems, smartphones, digital cameras, music players, digital video camcorders, and more. The size of a typical SD card is 24.0 (W) x 32.0 (L) x 2.1mm (H) and weighs about 2 grams.
SD cards are non-volatile memory cards that have nine pins (electrical contacts) and a write-protect switch. The first SD card introduced had a capacity of 2 GB but with ongoing development. New variations were released to offer more capacity than its predecessor. As a result, the original SD cards were discontinued and replaced by the newer-generation SDHC and SDXC cards. The newer variations of SD card like Secure Digital High Capacity (SDHC), Secure Digital eXtended Capacity (SDXC), and Secure Digital Ultra Capacity (SDUC) were designed to offer much higher capacity than a standard SD card.
How does an SD card work?
An SD card is based on flash technology that is also used by USB flash drives and high-speed desktop computers. These memory cards use flash memory storage chips to store data. The SD card comprises a very small circuit board that uses electronic current to store and retrieve data. The data stored on the card can be accessed with a USB card reader. Users need to insert the card in the card reader and connect It to a computer to access and modify the stored files. If used under ideal conditions, an SD card may have a shelf life of 10 years or more. To prevent the loss of data on your SD card, it is wise to back up your files after every photo or video session as these cards tend to become corrupted over time.
Data in an secure digital card is stored on a series of electronic components called NAND chips. All SD cards have a microcontroller that communicates with the device. This microcontroller works only when a user needs to save or retrieve data. Unlike other storage devices, SD Cards have no moving parts, which makes them less prone to damage when dropped. These cards use NAND storage that allows users to write and rewrite data thousands of times during the lifetime of the card.
SD card speed class and ratings
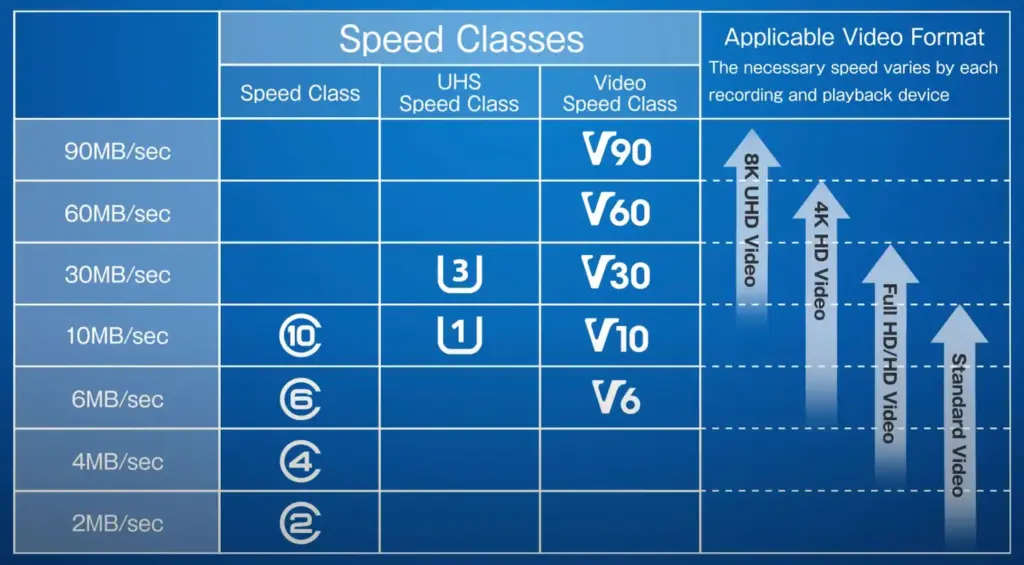
Unless you’re a tech geek, you must have confusion around secure digital card speed classes. SD card speed class specifies how different SD, miniSD, and microSD cards are rated in terms of the read and write speeds. The SD Association has defined three kinds of Speed Classes: “Speed Class”, “UHS Speed Class” and “Video Speed Class.” SD card speed classes define the “minimum speed” a given SD card should meet when reading or writing.
The SD card Speed Class, such as speed ‘Class’ 2, 4, 6, and 10 refers to the minimum write speeds. This means that cards can be rated as Class 2 (minimum write speed of 2MB/s), Class 4 (4MB/s), Class 6 (6MB/s), or Class 10 (10MB/s). The older cards that are not rated are referred to as ‘Class 0’. The speed class specified the minimum speed, which means that it’s possible for a card can achieve faster speeds. The Speed Class higher than 10 comes in the category of U1 and U3.
Which are referred to as UHS Speed Class. Under UHS Speed (Ultra High Speed) Class, UHS Speed Class 1 supports a minimum 10MB/s write speed, while UHS Speed Class 3 supports at least 30MB/s write speed. This is specified as either a 1 or 3 inside U symbol. For high-resolution video recording and to support next-generation flash memory like 3D NAND, there is Video Speed Class. The Video Speed Classes are V6, 10, 30, 60, and 90.
Some secure digital card manufacturers also mention “speed ratings” which should not be confused with “speed class”. Unlike the speed class which specifies minimum write speed, the speed rating indicates the “maximum speed” for reading and writing. So, a Class 10 memory card can also be listed as ‘up to 80MB/s’. In addition to this, the card might also be specified as, for example, ‘533x’ which is a multiplication of the speed of an old CD-ROM (150KB/s). This means that the SD card’s speed is 533 x 0.15 = 80MB/s (1,000KB in a MB). You can check the Speed Class of an SD card near the SD logo on the card and it is specified as a number inside a circular “C” shape. For the UHS Speed Class, look at the right of the SD logo, where it is denoted by a number inside a “U” shape.
Application performance class

You may also find a new A1 and A2 speed rating on some of the newer SD and microSD cards. All the classes- Speed Class, UHS Speed Class, and Video Speed Class rate cards to meet or exceed a minimum threshold for sequential write speed. These days, most users need memory cards to extend the memory of devices like smartphones and gaming consoles that run apps. These apps have different memory requirements, which means that instead of streaming sequential data. These apps write small chunks of data wherever they find available space. Given the demand for random read/write, instead of sequential read/write.
The SD Association introduced a new rating system known as the Application Performance Class Specification. Application Performance Class A1 and A2 were introduced to allow users to run applications on their mobile devices. Unlike cards that measure the speed in megabytes per second, A1 and A2 cards measure speed in “IOPS” (input-output access per second).
Bus interface speed
The Speed Class specifies the card’s minimum speed, while the Bus Interface Speed indicates the maximum possible data transfer speed between SD host devices and memory cards. Initially, SD1.0 was the Default Mode with a bus speed of 12.5MB/s. This was improved with the introduction of High-Speed Mode SD1.1 with a 25MB/s bus speed to support digital cameras. Over the years, SD Bus Interface specification has been increased from High Speed (25MB/s) to 3rd Generation of Ultra-High-Speed UHS-III (624MB/s). The SD Association introduced UHS-I, UHS-II, UHS-III, and SD Express to support new and faster devices. The SD Express uses the PCIe Gen.4 Interface with NVMe Protocol to deliver the fastest (3940MB/s) data transfer rates.
File systems and compatibility
When it comes to file systems, the SD Association has specified three file systems for the corresponding SD card types. FAT file systems are standardly used for all memory cards. FAT32 was introduced to replace the older FAT16 file system. Extended File Allocation Table (exFAT) is a modern replacement for FAT32 and is used in devices greater than 32GB.
SD card security
All secure digital cards have content protection technology (CPRM) that protects data on the device from illegal copying. However, this copyright protection feature CPRM doesn’t work automatically. To protect the data, users need to create a Media Identifier and Media Key Block (MKB) on the SD card. Furthermore, to protect data, some SD card has data protection features. Some manufacturers offer SD card that has a switch on the left side to turn on “write protection” which means that the card can only be read, and no data can be written. In the case of accidental file deletion or SD card formatting, data is not deleted per se. Only that space on a memory card is marked as available when an image is deleted. Users may lose data if they overwrite that space by storing new data.

